Aid procedure initiated for identified airports by the Commission.
Bremen, Germany - The ongoing infestation of the box tree moth in the green space at Bremen Airport has led to clearing work, with the current efforts expected to be completed by the end of the week. The costs of these current works are approximately 10,000 euros.
The infestation, which has been ongoing in the boxwoods of the park, has necessitated the removal of infested plants. However, the removal has been postponed for nature conservation reasons. After the removal of boxwoods, a temporary uniform lawn will be created.
The park is set for a redesign and adaptation to changed climate and biodiversity conditions in the long term. The participating departments for economy, construction, and environment, along with Bremen Airport, will jointly decide on the future design of the park.
The focus areas for the potential redesign include climate adaptation, strengthening biodiversity, improving the quality of stay for airport guests and employees, and maintenance costs. A decision on the future design of the park is still pending.
The current work provides an opportunity to fundamentally review the design of the park. Maintenance measures in the park have been limited to ensuring traffic safety until the start of the clearing season. The current work is being conducted by Bremen Airport GmbH and WFB Wirtschaftsförderung Bremen GmbH.
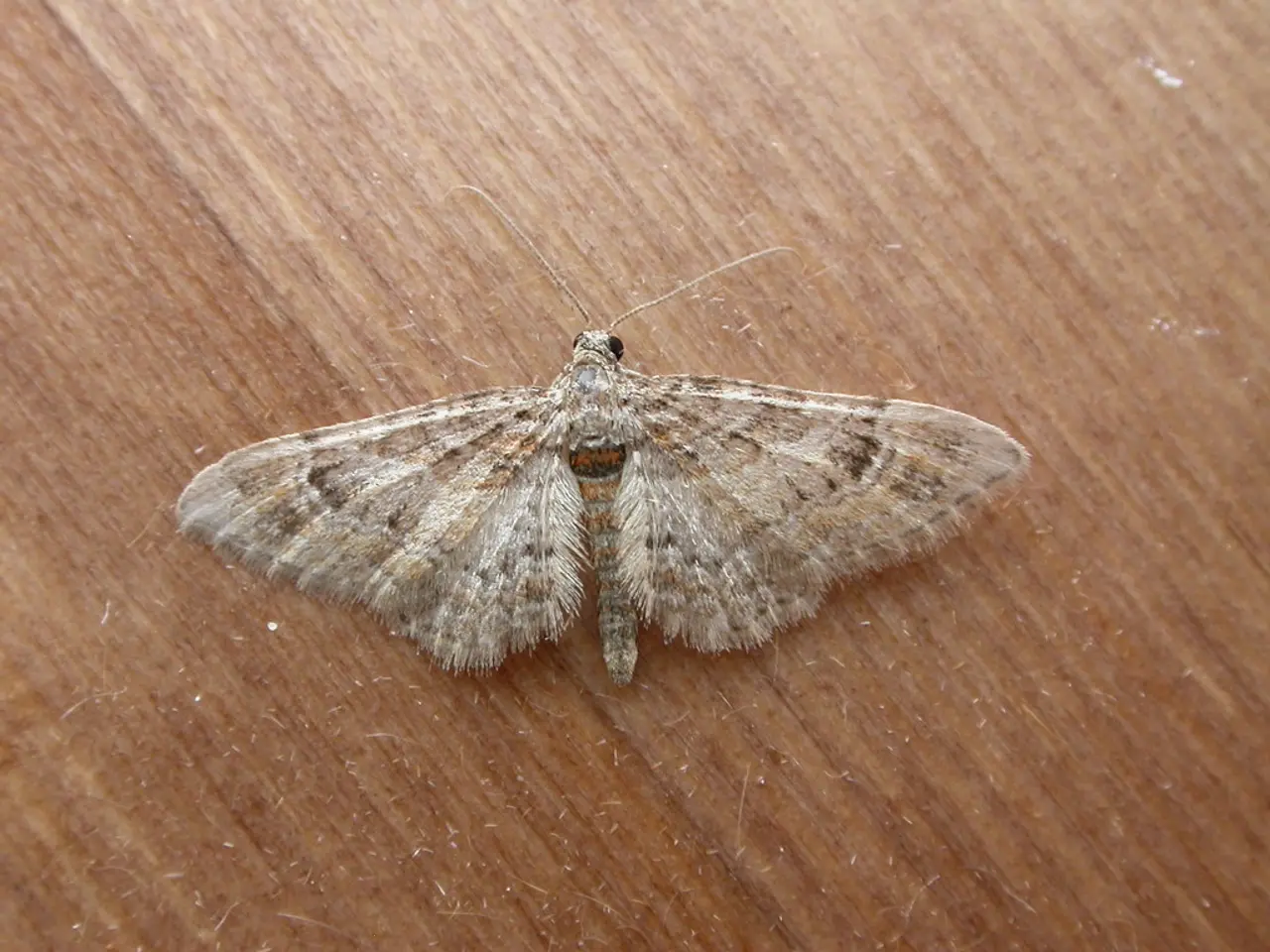
The box tree moth (Cydalima perspectalis) is an invasive pest that severely damages boxwood plants by defoliation. Infestations in public green spaces like parks can reduce plant health and aesthetic value, requiring management and redesign to mitigate damage.
Typical impacts and responses to box tree moth infestation might include significant defoliation of boxwood plants leading to weakened vegetation, loss of biodiversity, and altered park aesthetics. This can affect visitor experience and require intensive pest control efforts.
Plans often shift towards planting less vulnerable species, diversifying plant selection to reduce the risk of widespread damage, and redesigning landscapes to be more resilient. Removing or replacing infested boxwoods is common.
Incorporating species diversity and native plants more tolerant to local pest pressures and climate conditions, as well as implementing integrated pest management (including biological controls) to reduce chemical pesticide use, may be part of the long-term adaptation measures for the park.
For precise information on the local impact of the box tree moth infestation at Bremen Airport park, future design decisions, or climate adaptation measures, consulting local environmental reports, Bremen Airport authority releases, or municipal park management sources would be necessary.
- In light of the ongoing box tree moth infestation, the park’s future design will prioritize climate adaptation, environmental science, and biodiversity.
- To mitigate the impact of climate-change on the park, the focus will be on planting more resilient species and incorporating native plants that are tolerant to local pest pressures.
- The park redesign will also include improving the business aspects by considering the quality of stay for airport guests and employees, as well as maintenance costs.
- As part of the long-term adaptation measures, the park may shift towards integrated pest management and reduce the use of chemical pesticides, with the aim of ensuring environmental sustainability and promoting finance-friendly solutions within the aerospace and business industries.