The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) refers to the significant state-owned organization responsible for China's space technology development.
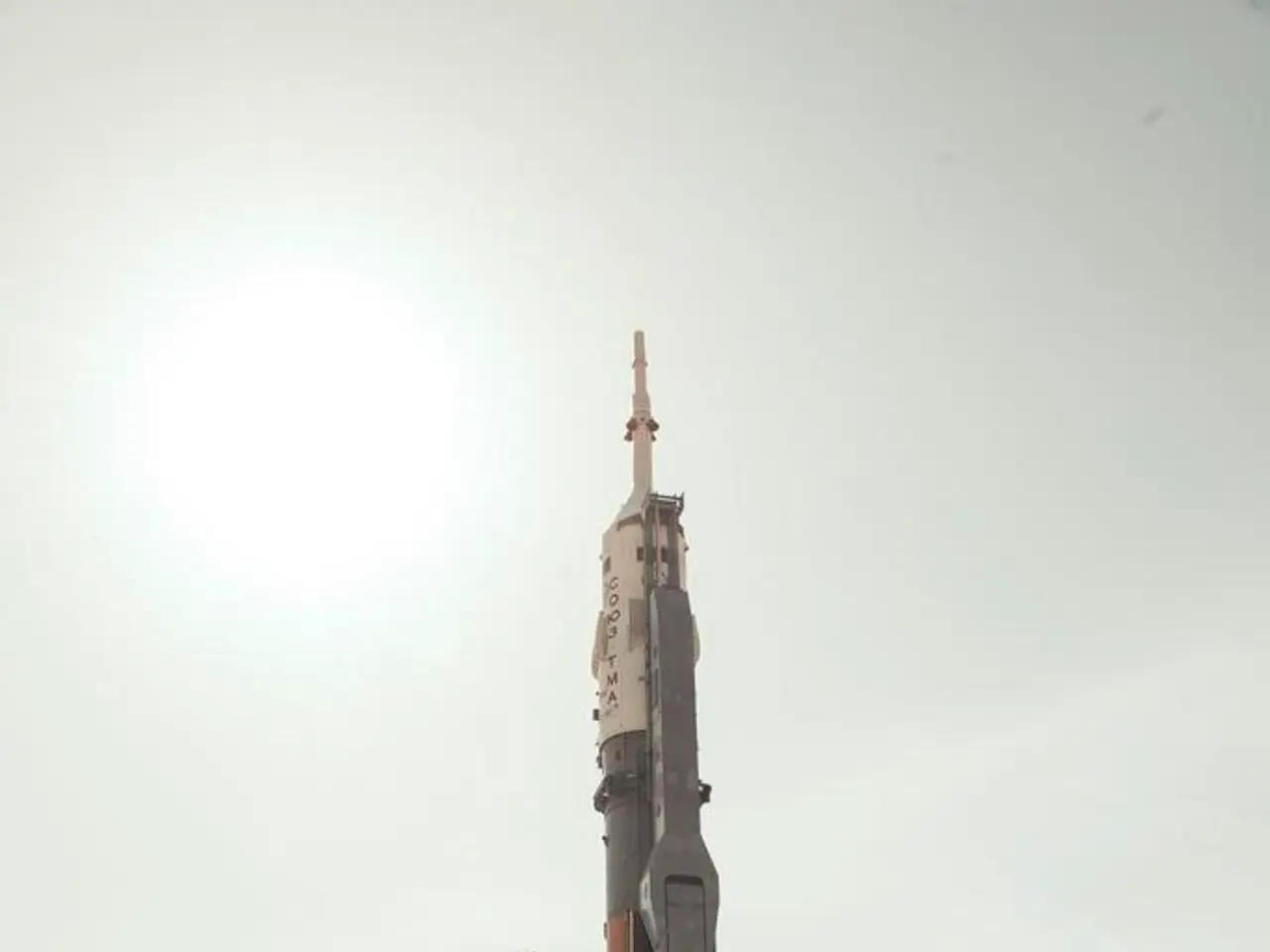
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) has played a central and pivotal role in the development and execution of China’s space program since its establishment. CASC, a Chinese state-owned space and defense conglomerate, is the primary entity responsible for designing, developing, and manufacturing China’s launch vehicles (rockets) and many of its satellites.
A Glimpse into CASC's History
China’s space efforts began in the mid-1960s, catalyzed by Chairman Mao Zedong’s directive to develop indigenous space technology. CASC was later established as the main corporate body executing China’s space agenda, working under the coordination of the China National Space Administration (CNSA). CASC inherited the responsibility for rocket and satellite development, enabling China to expand its space capabilities steadily.
Roles and Responsibilities of CASC
Launch Vehicles and Rockets
CASC designs and manufactures the entire family of Chinese launch vehicles, which are crucial for satellite deployment, cargo delivery to the Tiangong space station, and interplanetary missions.
Satellite Development
CASC develops various satellite types, including navigation, communication, Earth observation, and scientific research satellites. It is notably responsible for the Beidou Navigation Satellite System, China’s counterpart to GPS.
Space Missions and Exploration
CASC executes large-scale missions such as lunar sample return missions (e.g., Chang’e-6), asteroid sample return missions (Tianwen-2 launched in 2025), and supports the constructing and supplying of the Tiangong space station for human spaceflight.
International Cooperation
CASC promotes peaceful space utilization and supports China’s growing international cooperation programs, inviting partnerships for space exploration and research with over 30 countries.
Strategic Importance
CASC is at the heart of China’s rapid space program expansion, supported by a workforce exceeding 170,000, which allows sustained high mission frequency and growing ambition. This includes planning for both crewed and robotic missions, satellite constellation deployments, and scientific exploration projects beyond Earth orbit.
In summary, CASC acts as the technological and industrial backbone of China’s space endeavors, translating political and scientific ambitions into concrete hardware and operations that have placed China among the leading spacefaring nations globally within the last few decades.
CASC's work is not limited to China's borders; it has partnerships with foreign space firms and agencies, offering launch services and satellite technology to other countries. One of CASC's best-known products is the Long March series of rockets, used to carry satellites, spacecraft, and astronauts into orbit.
CASC is also investing in research on advanced propulsion systems, new spacecraft designs, space-based services, space biology experiments, new satellite electronics, miniaturization, and special materials. The corporation operates dozens of research and manufacturing centers across China and is run as a state enterprise under government supervision.
As CASC continues to push the boundaries of space exploration, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role in China's strategic vision of becoming a major "space power." Plans for lunar exploration, including robotic bases and eventual crewed missions around the Moon, sample-return missions to Mars and asteroids, and mega-constellation projects to beam broadband internet from low Earth orbit, are just a few examples of the ambitious projects underway.
References: 1. China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) (2021). China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. Retrieved from https://www.china-casc.com/ 2. Scharping, D. (2021). China's space agency: China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). DW. Retrieved from https://www.dw.com/en/chinas-space-agency-china-aerospace-science-and-technology-corporation-casc/a-58884110 3. Zhang, Y. (2021). China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC): A Brief Overview. The Diplomat. Retrieved from https://thediplomat.com/2021/09/china-aerospace-science-and-technology-corporation-casc-a-brief-overview/ 4. China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) (2021). History of China's Space Program. Retrieved from https://www.china-casc.com/en/history/ 5. National Space Science Center (2021). The History of China's Space Program. Retrieved from https://en.nscc.ac.cn/history-of-chinas-space-program/
- The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) has been instrumental in developing China's indigenous space technology since the mid-1960s, following Chairman Mao Zedong's directive.
- CASC, a Chinese state-owned space and defense conglomerate, is the primary entity responsible for designing, developing, and manufacturing China’s launch vehicles and many of its satellites.
- CASC's roles extend beyond China, offering launch services and satellite technology to other countries, while also promoting peaceful space utilization and international cooperation for space exploration and research with over 30 countries.
- Space-based services, space biology experiments, new satellite electronics, miniaturization, and special materials are among the advanced technologies that CASC is currently researching.
- CASC's influence is evident in China's strategic vision of becoming a major "space power," with plans for lunar exploration, Mars and asteroid sample-return missions, and mega-constellation projects to provide broadband internet from low Earth orbit.
- CASC's workforce exceeds 170,000, enabling sustained high mission frequency and growing ambition in both crewed and robotic missions, satellite constellation deployments, and scientific exploration projects beyond Earth orbit.
- The corporation operates dozens of research and manufacturing centers across China and falls under government supervision as a state enterprise, contributing significantly to China's space economy, science, industry, and finance.