Trump's reduction in foreign aid and its influence on worldwide HIV prevention efforts
In a significant blow to global HIV/AIDS efforts, the cuts to funding under President Trump's administration have had profound implications, particularly for high-risk populations.
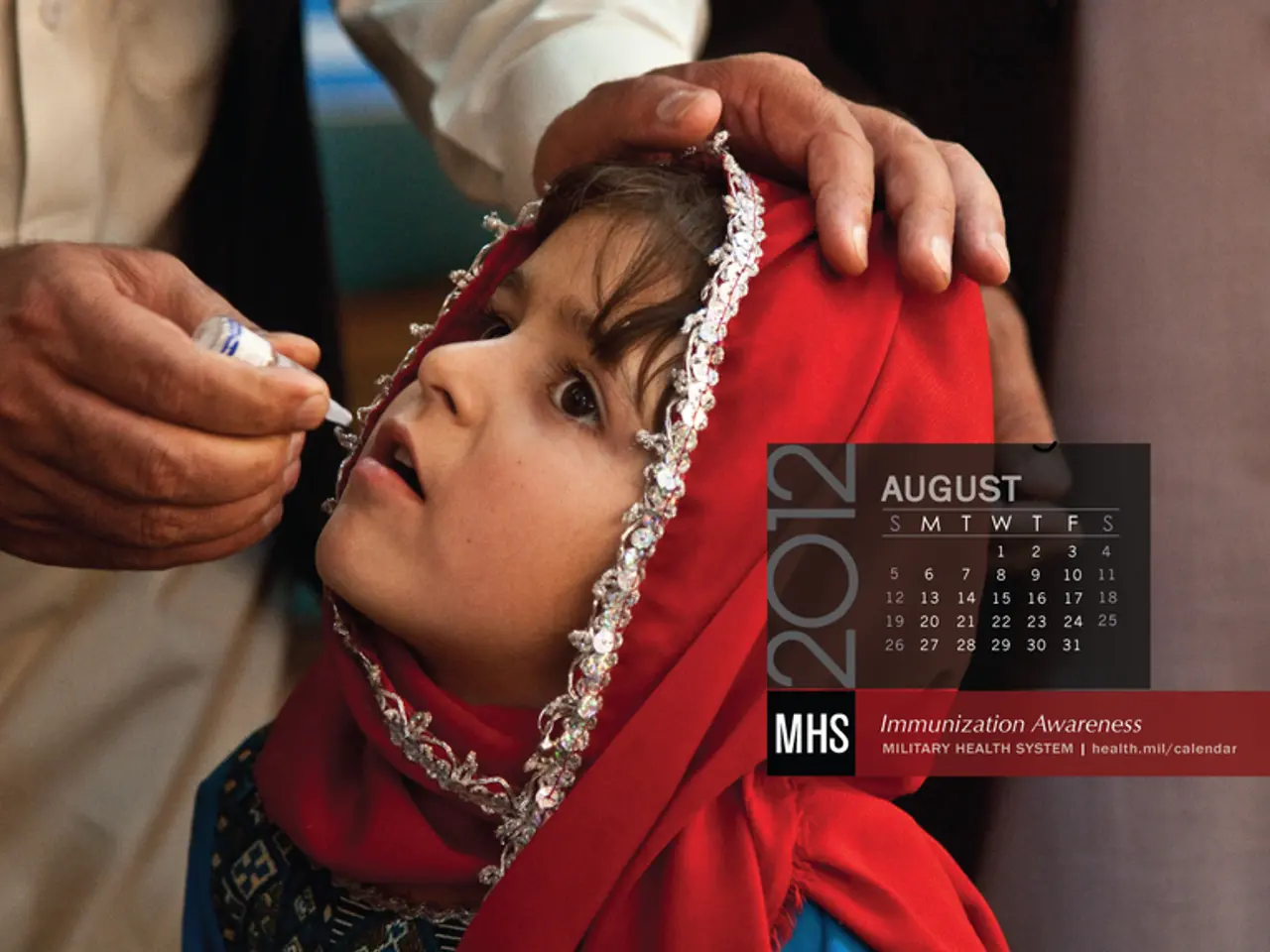
Since its launch in 2003, the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) has been a beacon of hope, investing over $110 billion, providing 64 million HIV tests, and saving 25 million lives in 55 countries, according to the State Department. However, the reduction in funding has led to a reduction in the capacity to provide effective prevention and care for these same vulnerable groups, undermining progress made in controlling the epidemic.
The cuts have disrupted ongoing HIV/AIDS programs, leading to setbacks in prevention, care, and support services for marginalized communities such as LGBTQ+ individuals. These groups often face compounded stigma and discrimination in healthcare access globally, and the pandemic context has further intensified these challenges, increasing barriers to healthcare and social support.
Experts warn that stopping PrEP and prevention services for high-risk populations could lead to continued spread of the virus. In fact, many sites catering to these groups have closed due to the cuts, and the number of new HIV infections in 2021 was 1.3 million, according to UNAIDS. Countries like Malawi, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique have almost entirely relied on PEPFAR for their prevention efforts.
The Trump administration has cancelled more than 80% of HIV/AIDS programmes led by the US Agency for International Development (USAID). While the US State Department continues to fund life-saving HIV treatment and testing, many groups most at risk of an infection, such as gay and bisexual men, sex workers, trans people, people who inject drugs, and incarcerated people, are now excluded from PEPFAR-funded PrEP. As a result, at least 3.5 million such people have lost access to PEPFAR-funded HIV prevention in the past six months.
The impact of these cuts is far-reaching. HIV-related deaths have decreased by more than half compared to 2010 levels, but the potential for a rise in HIV-related deaths and a resurgence of the HIV/AIDS epidemic looms large. The cuts could potentially lead to a broader spread of the virus, as infectious diseases tend to do, and could potentially reverse progress made in the fight against HIV/AIDS over the past few decades.
In March, US Congress failed to reauthorise PEPFAR, raising questions about its future, though the programme has funds until September 2025. The limited waiver in February permitted "life-saving" treatment services funded by PEPFAR to resume, but pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) medicine remains curtailed for most people.
Despite these challenges, experts stress the importance of maintaining and increasing funding for HIV/AIDS prevention, care, and treatment. The fight against HIV/AIDS is far from over, and continued investment is crucial to ensuring the progress made is not undone.
References: [1] UNAIDS. (2021). UNAIDS Data 2021. Retrieved from https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/databases/unaids-data-2021
[2] Kates, J. (2020). The Impact of Trump's HIV/AIDS Funding Cuts on Vulnerable Populations. Retrieved from https://www.kff.org/global-health-policy/perspective/the-impact-of-trumps-hivaids-funding-cuts-on-vulnerable-populations/
[3] PrEPWatch. (2021). Data Update: People Losing Access to PEPFAR-funded HIV Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.prepwatch.org/data-update-people-losing-access-to-pepfar-funded-hiv-prevention/
- Climate change poses a significant threat to global public health, exacerbating medical-conditions such as chronic diseases and cancers.
- SDG aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages, targeting various health-related issues including respiratory conditions, digestive-health, eye-health, and hearing.
- Science and medical-research play a crucial role in understanding and addressing the impact of climate change on health, particularly with regards to the rise in allergies and asthma due to pollen variability.
- Fitness-and-exercise, a key component of health-and-wellness, can help mitigate the effects of climate change on cardiovascular-health.
- Sexual-health is another critical aspect of health-and-wellness, with certain climates impacting the prevalence of sexually-transmitted infections.
- Autoimmune-disorders could be influenced by climate change, as shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the environment and potentially trigger flare-ups.
- In the context of climate change, commitment to renewable-energy is vital for maintaining industry standards and safeguarding our health and environment.
- Mental-health issues, including anxiety and depression, have been linked to climate change, stressing the need for therapies-and-treatments and increased support for mental-health awareness.
- Nutrition plays a significant role in health outcomes, with climate change affecting food availability, quality, and access.
- Climate change's impact on water resources can have serious consequences on digestive-health, eye-health, and overall hydration levels.
- Addressing skin-conditions that worsen due to extreme weather conditions, such as sunburn, requires increased focus on dermatological-research and sun protection measures.
- The retail industry can reduce its carbon footprint through sustainable practices, promoting environmental-science and contributing to the fight against climate change.
- Public-transit and carpooling schemes are crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
- Entrepreneurship in the field of renewable-energy can create new job opportunities and stimulate economic growth, while addressing the climate change crisis.
- Transportation choices, such as cycling or using electric vehicles, can help reduce carbon emissions and lessen the impact of climate change on respiratory-conditions.
- Leadership in the climate change fight requires vision, action, and collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and communities.
- Investing in renewable-energy projects can generate returns while reducing reliance on fossil fuels, thereby addressing climate change and financial portfolio diversification.
- The housing-market can be optimized to promote energy efficiency and sustainable living, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts and reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Venture-capital and private-equity firms can invest in technology startups that focus on renewable-energy, helping drive innovation and combat climate change.
- Personal-finance management should incorporate climate change risk assessment, guiding financial decisions and investments that support a low-carbon economy.
- Banking-and-insurance sectors are adapting to climate change risks by implementing climate stress tests and underwriting climate-related investments.
- Finance organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors in guiding their investment decisions and managing risks associated with climate change.
- Fintech innovation is enabling more efficient and sustainable energy use, paving the way for a more sustainable future and addressing climate change.
- Real-estate development can incorporate smart-home devices and building designs that promote energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- The automotive industry is transitioning towards electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and help combat climate change.
- Small-business owners can embrace the green economy by implementing sustainable practices and reducing their carbon footprint.
- CBD, derived from cannabis, is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic benefits for neurological-disorders like epilepsy and anxiety, but further research is needed.
- The impact of climate change on our ecosystem can lead to an increased prevalence of infectious diseases, as was seen with the outbreak of West Nile virus linked to flood waters.
- Climate change can contribute to worsening conditions in developing countries, exacerbating the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
- To address the challenges of climate change, it is essential for governments, businesses, individuals, and society as a whole to work together, embracing diversity-and-inclusion and collective action in the pursuit of a sustainable and healthy planet for future generations.