Unveiling Surveillance During the Cold War and the Debatable Employment of Contraband Aircraft Designs in the Creation of Supersonic Commercial Jets
In the annals of aviation history, the race to achieve supersonic flight for commercial airliners has been a captivating chapter. Two iconic aircraft, the Concorde and the Soviet Tu-144, often find themselves in the spotlight due to their striking similarities and the intriguing allegations of espionage that surround their development.
The Tu-144, often nicknamed the 'Concordski', shares several design features with its Western European counterpart. Both aircraft boast slender fuselages and ogival delta wing shapes, albeit the Tu-144's wing design is simpler, leading to poorer low-speed control. However, the Tu-144's powerplant is heavy with longer engine intakes, and it uses different engines, resulting in performance differences including shorter range.
The evidence supporting the claim that the Tu-144 was a 'clone' of the Concorde is primarily based on these notable outward similarities and allegations of Soviet espionage involving the theft of Concorde blueprints during the Tu-144's development. Western European journalists coined the nickname 'Concordski' due to the Tu-144’s strong resemblance to the Concorde.
However, despite these similarities, the Tu-144 had significant technical and performance differences. It required braking parachutes to land and experienced poor handling at low speeds. Its structurally automated production method also resulted in less safe design compared to the Concorde.
The Tu-144's service history was short, with only 55 passenger flights before being withdrawn following two crashes, reflecting challenges tied to this rushed and partly derivative design.
Meanwhile, the development of the Concorde was not exempt from the espionage activities rampant during the Cold War. The Concorde's development was not only challenged by the Tu-144 team but also by the Boeing 2702 and Lockheed L-2000, both of which were ultimately cancelled during the development process.
Interestingly, a recent documentary called 'Concorde: The Race for Supersonic' aired on Channel 4 in the UK, discussing the topic of the Concorde's competition and possible espionage. The practical use of Concorde blueprints for the Tu-144 development team was limited, as reflected in the final results.
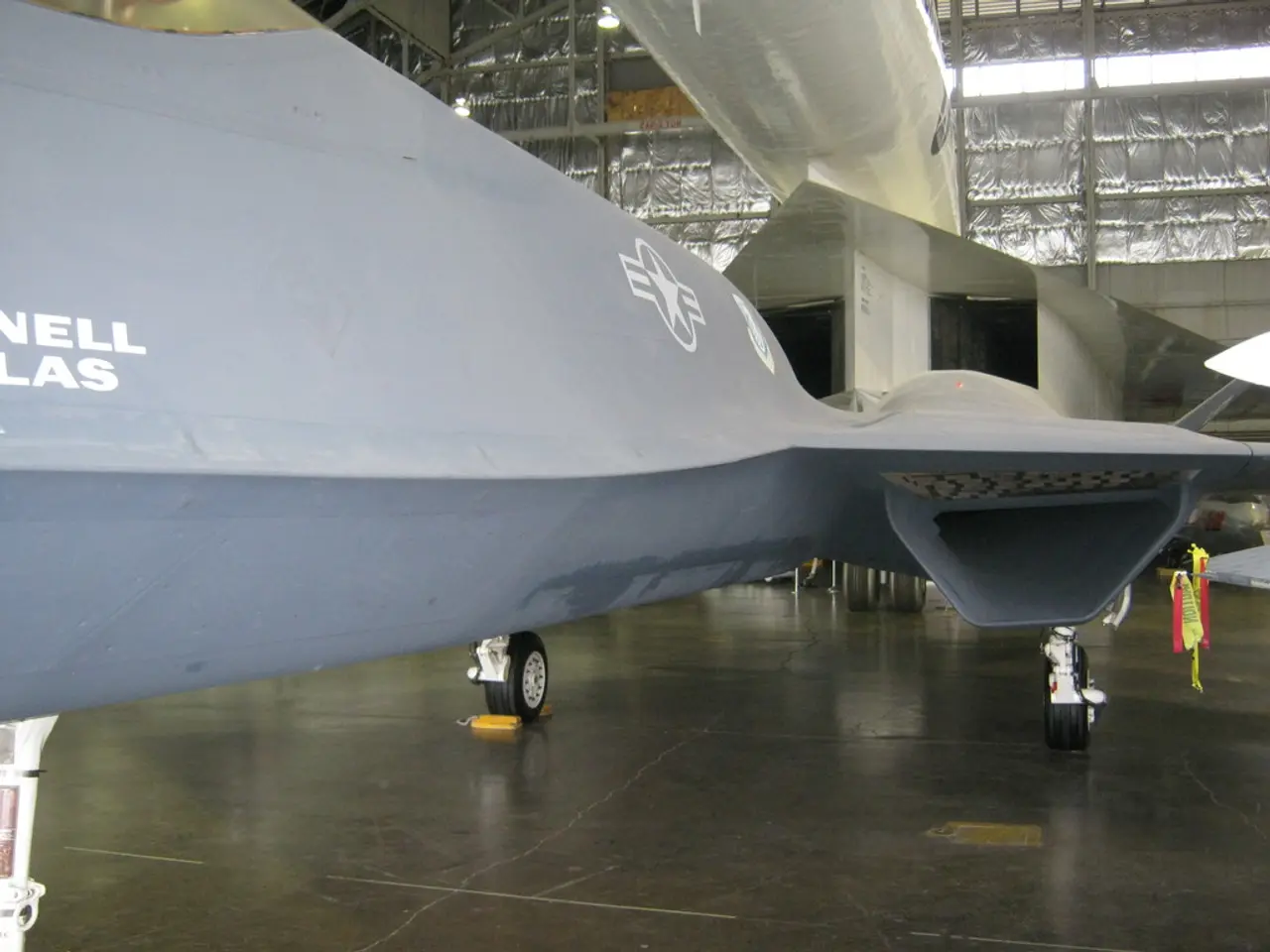
Fast forward to the present, a new player is entering the scene. The Lockheed Martin X-59 Quesst is being built for NASA to address the sonic boom and fuel usage issues that hampered supersonic flight. It remains to be seen if the X-59 Quesst will have the last laugh in the race towards supersonic flight for airliners, after the L-2000 lost to Boeing so many decades ago.
[1] Sources: "The Concorde and the Tu-144: A Comparative Analysis" by Aviation Historian Journal, "Concorde: The Race for Supersonic" documentary, and various academic articles on the history of supersonic aviation.
- The Tu-144, known as the 'Concordski', shares design similarities with the Concorde, but its simple wing design, heavier powerplant, and different engines caused it to perform differently, including having shorter range.
- The development of the Concorde was not only competitive but also involved espionage activities, as reflected by the unauthorized use of Concorde blueprints in the development of the Tu-144, according to allegations.
- The race for supersonic flight is not over yet, as the Lockheed Martin X-59 Quesst is being built for NASA to tackle issues like sonic boom and fuel usage that previously hindered supersonic flight, setting the stage for potential future victories in this ongoing competition.