World Health Organization Confirms Elimination of Malaria in Suriname
Suriname, a small South American country, has made history by becoming the first country in the Amazon region to eliminate malaria, according to a statement from the World Health Organization (WHO). This significant achievement was the culmination of two decades of sustained efforts and innovative strategies.
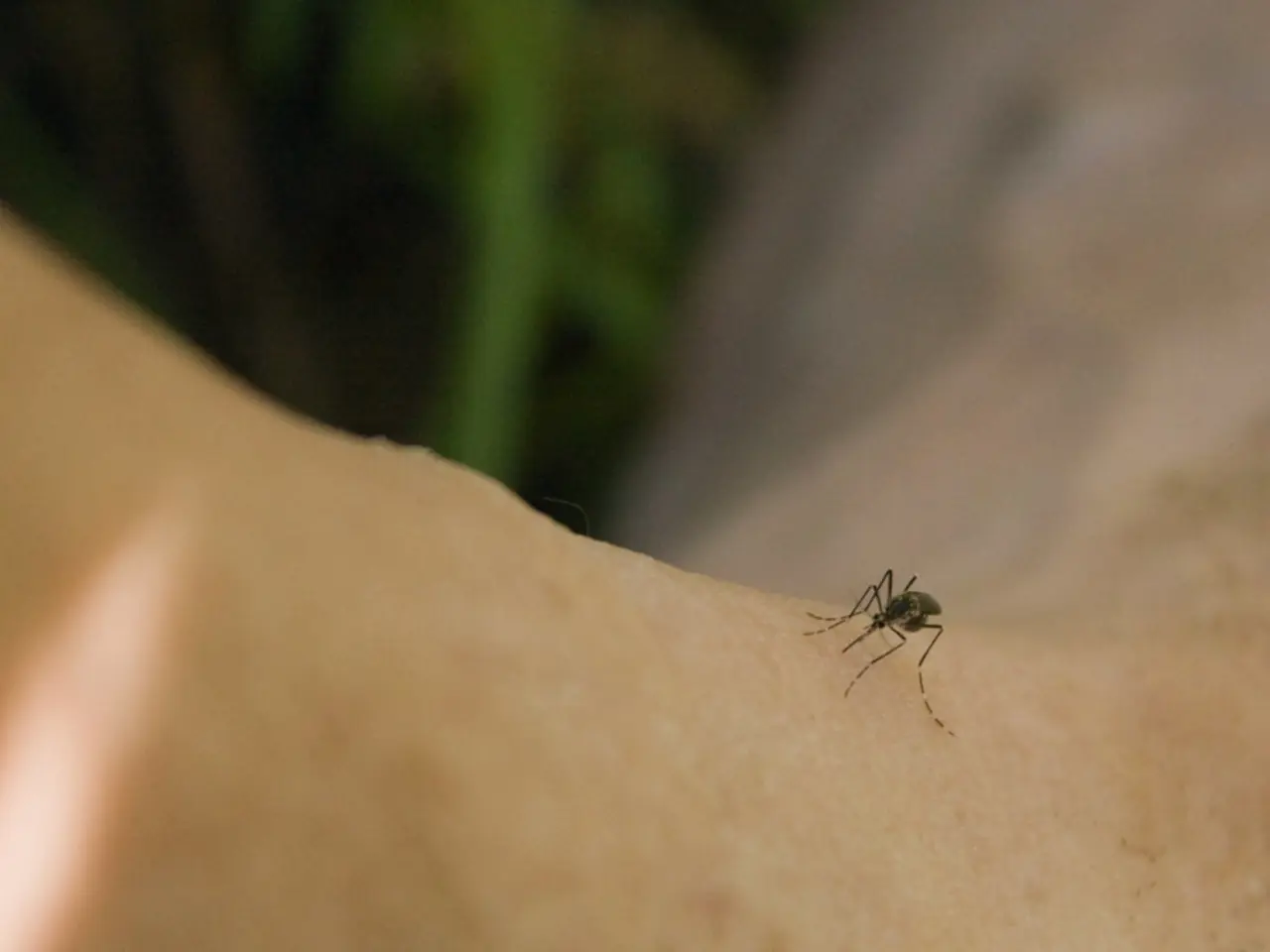
In the early 2000s, Suriname was grappling with a malaria epidemic. In 2001 alone, the country recorded 15,000 malaria cases, a stark reminder of the disease's prevalence. Malaria, one of the most common infectious diseases worldwide, is transmitted by mosquitoes and has been responsible for numerous deaths, particularly among children under five years old. In 2023, an estimated 263 million people in 83 countries contracted malaria, leading to 597,000 malaria-related deaths.
Suriname's journey towards malaria elimination began with a commitment from the government. They established a National Malaria Elimination Taskforce, a Malaria Program, and a dedicated Malaria Elimination Fund, ensuring continuous political and financial support. This commitment was further strengthened through regional collaboration with neighbouring countries, including Brazil, Guyana, and French Guiana.
Long-term technical cooperation from PAHO/WHO and the U.S. government also played a crucial role in strengthening Suriname's program capacities. The country was part of the “Elimination 2025” initiative, a global effort targeting malaria elimination by 2025.
One of the key challenges in Suriname was persistent malaria transmission among remote gold mining communities in the Amazon. To address this, Suriname implemented the Malakit intervention. This innovative approach involved distributing self-testing and self-treatment kits to miners. These kits included rapid diagnostic tests and artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) plus primaquine, ensuring prompt diagnosis and effective treatment adherence. This strategy led to a 43% decline in malaria incidence in the mining population between 2018 and 2020.
Alongside the Malakit project, years of targeted prevention campaigns and rapid case responses contributed to driving malaria cases down to zero. These efforts, combined with the government's sustained leadership and international cooperation, overcame the challenges posed by Suriname's dense forests and hard-to-reach areas.
On June 30, 2025, Suriname was officially certified malaria-free by the WHO, demonstrating that elimination is possible in challenging tropical, forested settings. This achievement serves as a beacon of hope for other countries still battling malaria, showcasing the power of sustained leadership, international cooperation, and innovative community-based strategies.
References:
- World Health Organization (2025). Suriname achieves malaria elimination. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news/item/30-06-2025-suriname-achieves-malaria-elimination
- Pan American Health Organization (2025). Suriname eliminates malaria. Retrieved from https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=14235:suriname-eliminates-malaria&catid=82:press-releases&Itemid=552
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2025). Suriname achieves malaria elimination. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/news/2025/suriname-eliminates-malaria.html
- United Nations Children's Fund (2023). Malaria: A persistent threat to children's health. Retrieved from https://www.unicef.org/health/malaria
- World Malaria Report (2023). World Malaria Report 2023. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/world-malaria-report-2023
- News of Suriname's elimination of malaria spread globally, marking a momentous victory in the field of workplace-wellness and medical-conditions.
- This accomplishment showcases the potential of countries to combat chronic diseases like malaria, offering a glimmer of hope for other nations still grappling with its impact.
- The significance of this success lies in its impact on cardiovascular-health, as malaria can contribute to heart complications.
- The success story of Suriname echoes the importance of fitness-and-exercise in preventing and managing a wide array of health-and-wellness issues.
- In the backdrop of the global rise in autoimmune-disorders, Suriname's elimination of malaria serves as a case study for the impact of effective therapies-and-treatments.
- The achievement also sheds light on the role of climate-change in shaping the prevalence and distribution of infectious diseases like malaria.
- The manufacturing sector can learn from Suriname's journey, as it highlights the importance of maintaining a focus on men's-health and workforce well-being.
- The success of Suriname's malaria elimination program underscores the need for mental-health initiatives in public health programs.
- The advancements in eye-health, hearing, and skin-care are indirectly connected to the elimination of malaria, as these conditions can be exacerbated by malaria-related malnutrition.
- The journey of Suriname towards malaria elimination serves as a reminder of the integral role of environmental-science in understanding and addressing health issues.
- In the era of cervical cancer and other gender-specific health issues, the success of Suriname's malaria elimination program highlights the importance of investements in womens-health.
- The achievement of malaria elimination offers valuable insights into effective parenting strategies, as the health of children is vital for overall health-and-wellness.
- In the context of the escalating weight-management crisis, the Suriname model offers a blueprint for integrating public health and weight management initiatives.
- The finance industry can learn from Suriname's success story, as it demonstrates the long-term benefits of sustainable investments in public health programs.
- The elimination of malaria in Suriname aligns well with the goals of energy savings, as malaria cases often peak during peak energy consumption seasons.
- Skin-conditions are closely linked to malaria, making Suriname's success story significant for dermatologists and skin-care practitioners.
- The success of Suriname's malaria elimination program has ripple effects on the space-and-astronomy community, as space exploration pose unique health challenges involving malaria.
- The aerospace industry can draw lessons from Suriname's journey, as its strategies can be adapted to address the health needs of astronauts and air travellers.
- Retail businesses can leverage Suriname's malaria elimination model to develop innovative strategies for ensuring the health and wellbeing of frontline workers.
- The achievement of malaria elimination underscores the importance of public-transit systems in promoting health and reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
- For small-business owners and entrepreneurs, Suriname's journey provides valuable insights into the role of leadership, diversity-and-inclusion, and adaptability in navigating complex challenges.
- The malaria elimination in Suriname has implications for the transportation sector, as health of drivers and passengers directly impacts safety and efficiency.
- The success of Suriname's malaria elimination program offers a case study for commercial real estate developers to prioritize health and wellness features in their properties.
- In the real-estate market, the Suriname model highlights the potential growth opportunities tied to health-conscious developments and investments.
- The achievement of malaria elimination has a significant impact on the housing market, as healthier living conditions reduce the incidence of related health issues.
- For banking-and-insurance professionals, Suriname's success story emphasizes the role of financial products and services in improving health and wellness outcomes.
- In the realm of fintech, Suriname's malaria elimination program demonstrates the potential of technology in facilitating access to healthcare and public health information.
- The elimination of malaria in Suriname has far-reaching implications for the stock-market, suggesting potential growth opportunities in the health industry and other sectors that prioritize employee wellness.